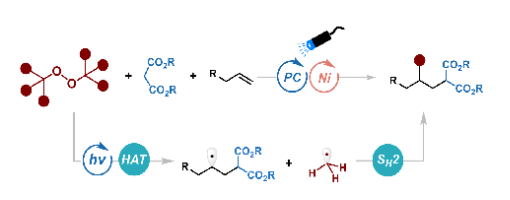
Hui Zhang, Ying-Jie Wang, Hao-Wen Jiang,* and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.5c05168
ABSTRACT: Herein, we report a strategy for the methylalkylation of unactivated alkenes via synergistic photoredox/nickel catalysis. This mild transformation employs di-tert-butyl peroxide (DTBP) as a bifunctional reagent, which serves simultaneously as a hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) reagent and a source of methyl radical, thereby facilitating the coupling of malonate-derived radicals with alkenes. By integrating HAT with radical selectivity control, the method enables the formation of two C(sp 3 ) bonds in a single synthetic operation, offering a streamlined route to valuable three-dimensional scaffolds.
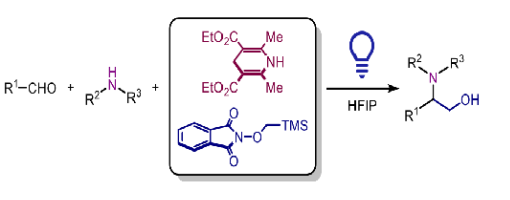
Ai-Lian Wang, Yi-Fan Yao, Xu-Gang Zhang,* and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.5c04773
ABSTRACT:
Herein, we report a catalyst-free, photosensitized strategy for synthesizing 1,2-amino alcohols. This transformation proceeds via the addition of an α-hydroxymethyl radical to an in situ-generated alkyliminium ion. The α-hydroxymethyl radical is formed by the radical Brook rearrangement of a (trimethylsilyl)- methoxy radical generated from an electron donor-acceptor (EDA) complex between Hantzsch ester and N-((trimethylsilyl)- methoxy)phthalimide. Therefore, this Mannich-type reaction establishes an additive-free, modular, and simple approach for the synthesis of 1,2-amino alcohols.
Saira Qurban, Hao-Wen Jiang, and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202501961
abstract
One of the most difficult issues facing humanity today is thetreatment of cancer. A binary cancer treatment called boronneutron capture therapy (BNCT) works especially well for high-grade gliomas and metastatic brain malignancies. Due to theirpreferential absorption by developing tumor cells, boronatedamino acids have drawn a lot of attention among the severalboron-containing compounds utilized as BNCT agents. In the first section of this review, the fundamental ideas of BNCT arebriefly presented. In the remaining sections, we present a thor-ough analysis and synthesis of several boronated amino acidsusing distinct techniques. This article summarizes the thera-peutic prospects of boron delivery agents and offers a criticalanalysis of them from the perspectives of nuclear medicinedoctors and medicinal chemists.
Teng-Fei Xiao, Ke-Rui Jian, Yu-Cheng Gu, Guo-Qiang Xu and Peng-Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5SC06987D
ABSTRACT
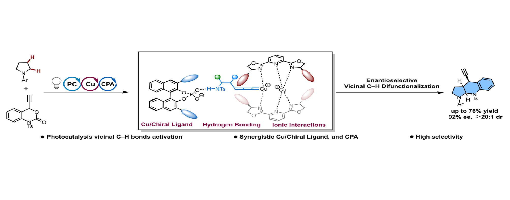
Existing strategies are typically limited to modifying a C–H site (a or b-position) of saturated cyclic amines, but the asymmetric difunctionalization of vicinal C–H bonds remains a formidable challenge. To address this challenge, this work introduces a synergistic catalytic system that merges visible-light photocatalysis with asymmetric copper and chiral phosphoric acid catalysis. This system enables the enantioselective synthesis of ring-fused amine skeletons by activating vicinal C–H bonds in straightforward saturated cyclic amines. The reaction proceeds in good yields (up to 76%) and excellent enantioselectivity (up to 92% ee). This work describes detailed mechanistic studies that identify the specific dual chiral catalytic system that forms the basis for the enantioselectivity.
Huan-Huan Zhao, Xu-Gang Zhang, Hao-Wen Jiang, Yi Zhao, Xiu-Qin Hu,*and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.5c03480
ABSTRACT:
Inthisstudy,wedevelopedavisiblelight-mediatedC(sp3)−Haminationstrategyenabledbyligand-to-metalcharge transfer(LMCT)andironcatalysis.TheinexpensiveFe(NO3)3·9H2Oaffordsaphotoactiveironcomplexuponcoordinationwith N-heteroarylsubstrates,andthecomplexundergoesLMCT-inducedβ-homolysistoproduceahigh-valentFe(IV)�Ospecies.The Fe(IV)�Ospeciespromotesalkyl radical formation,enablingefficientC(sp3)−Nbondconstruction.Thereactionoperatesunder mild conditionswithbroad functional group tolerance and excellent scalability, providing a practical platformforC(sp3)−H amination.

Xiang-Chuang Tan, Lei Yan, Hao-Ni Qin and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1039/D5GC03425F
Abstract
Herein, we report the development of a carbon-bound radical cyanating reagent, 2-methyl-2-(pyridin-2 yl)malononitrile (MPYMN), which enables metal-free photocatalytic cyanation with high reactivity and site selectivity. MPYMN is a bench-stable, readily accessible solid that does not release cyanide during reac tions nor does it require metals or harsh conditions. It exhibits superior performance compared to com mercially available cyanating agents and other carbon-bound cyanide sources. Importantly, the steric effect of the quaternary carbon in MPYMN facilitates reagent-controlled site-selective cyanation. The syn thetic utility of this reagent is demonstrated by its compatibility with both photoredox and hydrogen atom transfer (HAT) processes, including efficient late-stage functionalization of complex molecules relevant to medicinal chemistry.

Yi-Xiang
Geng, Teng-Fei
Xiao, Dong Xie, Ming-MingLi, Pan-Pan
Zhou, Guo-Qiang Xu*, Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-64399-7
Abstract
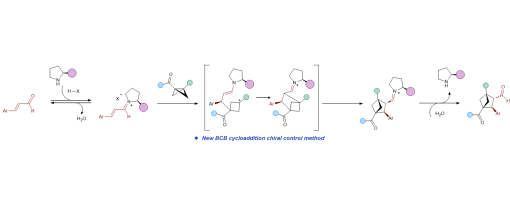
Bicyclo[2.1.1]hexanes (BCHs), three-dimensional benzene bioisosteres char acterized by high sp3-carbon content, hold great promise for diverse appli cations in medicinal chemistry. Although significantadvanceshavebeenmade in the synthesis of racemic BCHs, highly enantioselective approaches remain comparatively rare. Here we report a mild, secondary amine–catalyzed asymmetric [2π+2σ] cycloaddition of bicyclo[1.1.0]butanes (BCBs) with α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, whichovercomeskeylimitationsofexistingmetal catalyzed and photochemical methods. The protocol operates under ambient air and tolerates a wide range of BCB and aldehyde substrates bearing diverse functional groups, affording BCH scaffolds in yields of up to 84% under Supramolecular Iminium Catalysis with excellent enantioselectivity (up to 99% ee) and high diastereoselectivity (>20:1 dr). The mild conditions and opera tional simplicity underscore the potential of this transformation for stereo selective manufacturing of BCHs at scale. Mechanistic experiments and DFT studies support an acid-promoted dual activation of both substrates, followed by an enamine–iminium tandem catalytic process that delivers the enan tioenriched products.
Zhi Lei, Hao Tang, Heng Zhang, Yong-Chun Luo*, Peng-Fei Xu*
http://10.1016/j.psep.2025.107561
ABSTRACT
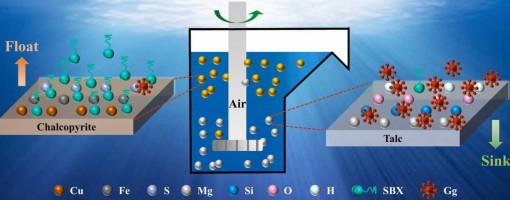
The intergrowth phenomenon of chalcopyrite and talc makes the identification of an eco-friendly and efficient depressant crucial for achieving effective separation. In this study, we innovatively employed Ghatti Gum as a talc depressant to improve the flotation separation. The micro-flotation test results demonstrate that, compared to conventional depressants, Ghatti Gum exhibits a stronger depressing effect on talc while maintaining excellent selectivity toward chalcopyrite. Atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy with energy- dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images confirmed that Ghatti Gum adsorbed selectively on the surface of talc, which significantly altered its surface roughness and elemental composition. In contrast, Ghatti Gum exerts a weaker influence on chalcopyrite. Further analysis through Zeta potential, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and density functional theory (DFT) calculations revealed that Ghatti Gum adsorbs onto the talc surface through hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Meanwhile, Ghatti Gum has less influence on the elemental composition and floatability of the chalcopyrite surface. In summary, Ghatti Gum emerges as a promising eco- friendly depressant for the flotation separation of chalcopyrite and talc. This discovery not only expands the applications of Ghatti Gum but also provides novel insights for the efficient separation of chalcopyrite from talc.
Zhi Lei, Heng Zhang, Hao Tang, Yong-Chun Luo*, Peng-Fei Xu*
http://10.1016/j.jece.2025.117093
Abstract
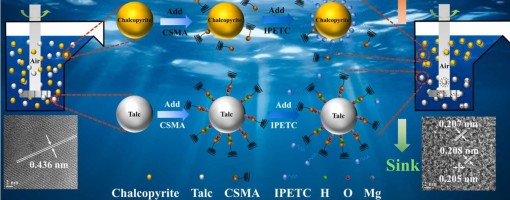
The flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc presents a significant challenge due to its analogous surface characteristics. This study investigated the selective depression of talc in the presence of chalcopyrite using a novel modified chitosan (CSMA), achieving effective mineral separation. CSMA possesses a porous architecture compared to unmodified chitosan (CS), which facilitates enhanced interaction with mineral surfaces. Flotation tests revealed that CSMA significantly inhibited talc flotation while exerting minimal impact on chalcopyrite recovery. Morphological and elemental changes were analyzed using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectroscopy (ICP-OES), atomic force microscopy (AFM), scanning electron microscopy with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). These analytical results confirm that CSMA adsorbs onto the talc surface. In addition, zeta potential measurements, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and density functional theory (DFT) calculations collectively indicate that CSMA exhibits enhanced reactivity, primarily through hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions with the talc surface. This investigation elucidates the mechanism by which carboxymethyl chitosan acts as an effective depressant in the flotation separation of copper sulfide minerals, thereby establishing a foundation for the environmentally friendly recovery of these minerals.
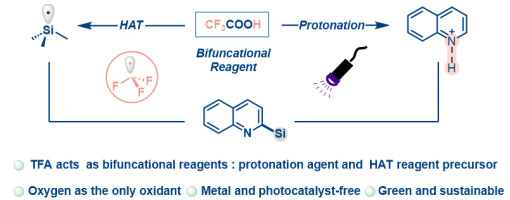
Rui Zhang, ‡ Hao-Wen Jiang, ‡ Xiu-Qin Hu, and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.5c03441
ABSTRACT:
A photoinduced Minisci reaction involving Si−H bond activation via a CF 3 radical generated from trifluoroacetic acid as a hydrogen atom transfer reagent has been achieved for the f irst time. This approach enables the synthesis of a diverse array of silylated electron-deficient heteroarenes in moderate to high yields. Mechanistic studies were conducted to provide supporting evidence for the reaction process. The reaction features a metal free protocol, operational simplicity, and compatibility with mild reaction conditions.