Organic Photoredox Catalytic α-C(sp3)–H Phosphorylation of Saturated Aza-Heterocycles
Ming-Jun Yi,‡ Teng-Fei Xiao,‡ Wen-Hui Li, Yi-Fan Zhang, Pen-Ji Yan, Baoxin Zhang, Peng-Fei Xu and Guo-Qiang Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC05767G
Abstract
A metal-free C(sp3)–H phosphorylation of saturated aza-heterocycles via the merger of organic photoredox and Brønsted acid catalysis was established under mild conditions. This protocol provided a straightforward and economic access to a variety of valuable α-phosphoryl cyclic amines by using commercially available diarylphosphine oxide reagents. In addition, the D-A fluorescent molecule DCQ was firstly used as a photocatalyst and exhibited excellent photoredox catalytic efficiency in this transformation. A series of mechanistic experiments and DFT calculations demonstrated that this transformation underwent a sequential visible-light photoredox catalytic oxidation/nucleophilic addition process.

Divergent Ritter-type amination via photoredox catalytic four-component radical-polar crossover reactions
Sheng-Qiang Guo, Hui-Qing Yang, Ai-Lian Wang, Yu-Zhen Jiang, Guo-Qiang Xu, Yong-Chun Luo,* Zhao-Xu Chen and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1GC03048E
A green and practical divergent Ritter-type amination via a photoredox catalytic four-component radical-polar crossover process was developed. This versatile protocol presents a modular and powerful strategy to access functionalized β-sulfonyl imides and imines under mild conditions from readily available and stable substrates with high atom-, step- and redox economy. We manipulated carboxylic acids and benzotriazoles to precisely attack the nitrilium ion instead of the carbocation, thus preventing many complicated side reactions of the photocatalytic reactions. Furthermore, the synthetic utility of this divergent Ritter reaction is further demonstrated by the late-stage modification of pharmaceutical and natural product derivatives.

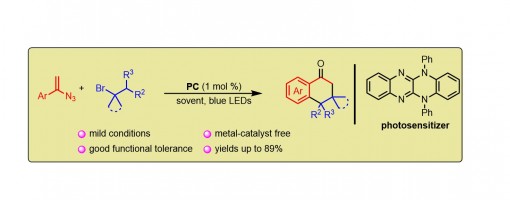
Visible-Light-Promoted Multi-step Tandem Reaction of Vinyl Azides toward the Formation of 1-Tetralones
Meng-Jie Jiao, Qiang Hu, Xiu-Qin Hu* and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c02261
ABSTRACT
A visible-light-driven multi-step tandem reaction between vinyl azides and alkyl bromides has been developed leading to the formation of tetralone skeletons under mild conditions, which can be easily scaled up to the gram scale. Various 1-tetralone derivatives are synthesized and transformed into desired products in good to high yields.
Dehydrogenation/(3+2) Cycloaddition of Saturated Aza-Heterocycles via Merging Organic Photoredox and Lewis Acid Catalysis
Teng-Fei Xiao, Yi-Fan Zhang, Wen-Tao Hou, Pen-Ji Yan, Jun Hai, Peng-Fei Xu*, and Guo-Qiang Xu*https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c03431
Abstract
Herein, we report a photoinduced dehydrogenation/(3+2) cycloaddition reaction by merging organic photoredox and Lewis acid catalysis, providing a straightforward and efficient approach for directly installing a benzofuran skeleton on the saturated aza-heterocycles. In this protocol, we also describe a novel organic photocatalyst (t-Bu-DCQ) with the advantages of a wider redox potential, easy synthesis, and a low price. Furthermore, the stepwise activation mechanism of dual C(sp3)–H bonds was demonstrated by a series of experimental and computational studies.

Visible-light organic photoredox catalytic cascade reaction
Guo-Qiang Xu* and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC04883J
Abstract
Over the past years, impressive progress has been made on the development of organic photoredox catalytic cascade reactions without the participation of expensive and toxic transition-metals under visible light irradiation. These transformations highly depend on the in situ generation of various radical species in the photoredox catalytic cycles. Numerous chemically and biomedically valuable building blocks have been synthesized through this efficient and sustainable protocol. In this review, we highlight the recent progress in this blooming area by presenting a series of new catalytic cascade reactions mediated by organic photoredox catalysts and describe their mechanisms and applications which have appeared in the recent literature.

Enantioselective Construction of Polycyclic Indazole Skeletons Bearing Five Consecutive Chiral Centers through an Asymmetric Triple-Reaction Sequence
Jia-Lu Zhang, Wen-Long Ye, Jie Zhang, Xiu-Qin Hu,* and Peng-Fei Xu*
DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.1c01559
ABSTRACT: A novel approach for the asymmetric construction of polycyclic indazole skeletons via enamine−imine activation and PCET activation was developed by merging organocatalysis with photocatalysis through an asymmetric triple-reaction sequence. In this process, five C−X bonds and five consecutive chiral centers were efficiently constructed. Differently substituted polycyclic indazole deriatives were successfully constructed with satisfactory results under mild conditions.

One-Pot Enantioselective Construction of Polycyclic Tetrahydroquinoline Scaffolds through Asymmetric Organo/Photoredox Catalysis via Triple-Reaction Sequence
Jia-Lu Zhang, Jin-Yu Liu, Guo-Qiang Xu, Yong-Chun Luo, Hong Lu, Chang-Yin Tan, Xiu-Qin Hu*, and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00712
Abstract
A novel one-pot triple-reaction strategy for the asymmetric construction of polycyclic skeletons with multiple consecutive chiral centers through aza-Michael/Michael/Wittig/ketyl radical addition/esterification processes is reported. A wide range of polycyclic tetrahydroquinoline derivatives were smoothly obtained from easily available starting materials with good results (up to 80% yield, >20:1 dr, >99% ee) under mild conditions. In this transformation, five chemical bonds and five consecutive chiral centers were successively formed.

Metal-Free α-C(sp3)–H Aroylation of Amines via a Photoredox Catalytic Radical–Radical Cross-Coupling Process
Guo-Qiang Xu*, Teng-Fei Xiao, Guo-Xuan Feng, Chen Liu, Baoxin Zhang, and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.orglett.1c00226
Abstract
Here we describe an unprecedented metal-free C(sp3)–H aroylation of amines via visible-light photoredox catalysis, which provides a straightforward route for the construction of a useful α-amino aryl ketone skeleton. Additionally, a number of selected products exhibit good biological activity for protecting PC12 cell damage, which shows that this skeleton has the potential to become a new neuroprotective agent. Finally, a series of mechanism experiments indicate that this transformation undergoes a photoredox catalytic radical–radical cross-coupling pathway.

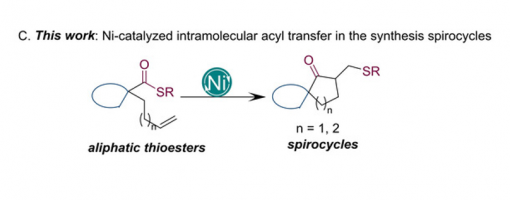
Synthesis of Spirocycles via Ni‐Catalyzed Intramolecular Coupling of Thioesters and Olefins
Wenfei Liu, Dr. Wenhua Xu, Juanjuan Wang, Dr. Hong Lu, Prof. Dr. Peng‐Fei Xu, Prof. Dr. Hao Wei
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202100390
Abstract
A nickel‐catalyzed intramolecular coupling of thioesters and olefins has been developed for the efficient synthesis of spirocycles, a privileged scaffold commonly found in natural products. This transformation is characterized by the simultaneous transfer of both acyl and thiol moieties to the alkene, with the suppression of decarbonylation and β‐hydrogen elimination. Initial mechanistic investigations are consistent with an oxidative addition/olefin insertion/reductive elimination mechanism. The incorporated methylene sulfide substituent can undergo a variety of further reactions to increase molecular diversity and complexity. These results demonstrate that thioester derivatives can be used as powerful building blocks for the assembly of complex scaffolds.
Nickel‐Catalyzed Intramolecular Decarbonylative Coupling of Aryl Selenol Esters
Jin‐Hua Bai, Xiu‐Juan Qi, Wei Sun, Tian‐Yang Yu, Peng‐Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.202001611
Absrtact
This report describes a method for Ni‐catalyzed intramolecular decarbonylative coupling, which enables the conversion of areneselenol esters to diaryl selenides. The inexpensive and readily available catalyst can be employed under mild reaction conditions for the construction of structurally diverse diaryl selenides, including heterocyclic and natural product derivatives.

Sc(OTf)3 catalyzed [3 + 2]-annulation reaction of donor–acceptor aziridines with methylene exo-glycals: synthesis of chiral carbohydrate-spiro-heterocycles
Jie-Hui Zhang, Cheng-Lin Pan, Huan-Huan Zhang, Peng-Fei Xu* and Yong-Chun Luo*
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1QO00228G
A Sc(OTf)3 catalyzed [3 + 2]-annulation reaction between donor–acceptor aziridines and several exo-glycals has been developed. Using this method, some exo-glycals derived from D-ribose, D-galactose and uridine can be converted into carbohydrate-spiro-heterocycles easily in good yields. Simple derivatization of the products gives proline analogues and polycyclic compounds. Moreover, this reaction disclosed the stereochemistry characteristic of the reaction between racemic D–A aziridines and chiral enolethers.

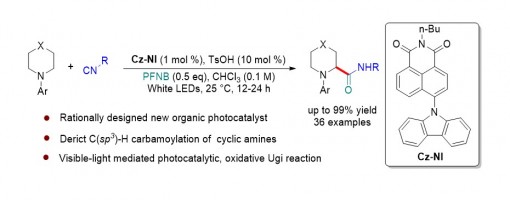
Ming-Jun Yi,§ Huan-Xin Zhang,§ Teng-Fei Xiao, Ji-Hua Zhang, Zhi-Tao Feng, Li-Pu Wei, Guo-Qiang Xu*, and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.1c00242
Abstruct
Herein, we report a general strategy for the rational design of an efficient organic photocatalyst, and we describe a robust method for the direct C(sp3)–H carbamoylation of saturated aza-heterocycles under mild conditions by using a naphthalimide (NI)-based organic photocatalyst. This protocol provides a concise and practical approach for the rapid installation of a valuable amide bond onto pharmaceutically useful saturated aza-heterocycles to access a wide range of cyclic α-amino amides. A series of mechanism investigations have demonstrated this transformation undergoes a visible-light photocatalytic, oxidative Ugi reaction process.
Jie Fang, Qiang Hu, Wan-Li Dong, Guo-Qiang Xu, Xiu-Qin Hu, Yong-Chun Luo, and Peng-Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.31635/ccschem.020.202000542
Abstract
Direct introduction of a carboxyl group into molecules is one of the most useful methods for the preparation of carboxylic acids, which avoids the conversions of various pre-existing functional groups and features good step- and atom-economy. However, the methods for the direct synthesis of two-carbon added carboxylic acids from the precursors remain rare. Herein, we first report a general and mild method for the direct synthesis of a range of aliphatic acids by photoredox catalyzed hydrocarboxymethylation of alkenes with good toleration of various functional groups, in which bromoacetic acid is utilized as an ideal two-carbon synthon. The synthetic utility of this hydrocarboxymethylation protocol is further demonstrated by the concise synthesis of two marketed drugs, sensipar and tirofiban, from commercially available starting materials.

Selective Decarbonylation via Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Carbon–Carbon Bond Cleavage
Hong Lu, Tian-Yang Yu, Peng-Fei Xu, Hao Wei*
https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00153