Cobalt-catalyzed chemoselective dehydrogenation through radical translocation under visible light
Wan-Lei Yu,Zi-Gang Ren,Ke-Xing Ma,Hui-Qing Yang, Jun-Jie Yang, Haixue Zheng, Wangsuo Wu and Peng-Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2SC02291E
The transformations that allow the direct removal of hydrogen from their corresponding saturated counterparts by the dehydrogenative strategy are a dream reaction that has remained largely underexplored. In this report, a straightforward and robust cobaloxime-catalyzed photochemical dehydrogenation strategy via intramolecular HAT is described for the first time. The reaction proceeds through an intramolecular radical translocation followed by the cobalt assisted dehydrogenation without needing any other external photosensitizers, noble-metals or oxidants. With this approach, a series of valuable unsaturated compounds such as α,β-unsaturated amides, enamides and allylic and homoallylic sulfonamides were obtained in moderate to excellent yields with good chemo- and regioselectivities, and the synthetic versatility was demonstrated by a range of transformations. And mechanistic studies of the method are discussed.

https://doi.org/10.1039/D2GC02084J
Direct C–H/N–H dehydrogenative coupling is a promising yet thermodynamically unfavorable transformation in the absence of a sacrificial hydrogen acceptor. Herein, a conceptually novel oxidant-free dehydrogenative amination of alkenes through a synergistic photoredox and cobalt catalysis with H2 evolution has been achieved. With this approach, a wide range of five-membered N-heterocycles were synthesized with excellent atom-economy. The green system will address the challenges that are sensitive to traditionally oxidative conditions. Furthermore, the scope and mechanistic details of the method are discussed.

Cheng-Lin Pan , Xiang-Xiang Wei , Xu-Gang Zhang , Yong-Wei Xu , Peng-Fei Xu* , Yong-Chun Luo*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107625
In this work, 2-((5-mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)acetic acid (MTAA), a stable and eco-friendly organic small-molecule reagent, was introduced as chalcopyrite depressant for selective flotation separation of molybdenite from chalcopyrite. In the flotation experiments of single mineral and artificially mixed mineral, the recovery of chalcopyrite reduces from 90% to 5% in the pH range of 5 to 10 when MTAA (8 mg/L) is added. The results of IR and zeta potential show that there are two tautomers (thione and thiol) in solid MTAA, while in aqueous solution, MTAA is mainly in the form of thiol and reacts with copper ions. The results of XPS and Tof-SIMS measurements indicate that MTAA may react with copper ions to form a quaternary chelate structure via the S and N atoms. The DFT calculation results also show that MTAA is more likely to react with copper ions than iron ions.

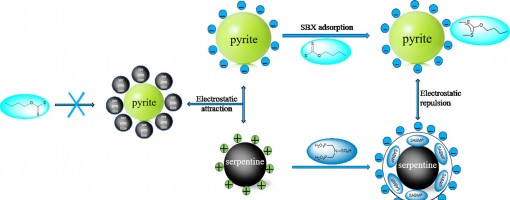
Xu-Gang Zhang , Jie Zhang , Wen-long Ye , Cheng-Lin Pan , Xiang-Xiang Wei , Xiu-Qin Hu , Yong-Chun Luo,* , Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107602
The flotation of pyrite is often depressed by the slime coating of fine serpentine. To eliminate the negative effect of serpentine, N,N-bis(phosphonomethyl)-sulfamic acid (SABMP) was employed as the depressant in this study. The results of micro-flotation experiments showed that the addition of SABMP could significantly reduce the adverse effect of fine serpentine and restore the floatability of pyrite in the pyrite-serpentine system. However, the floatability of pyrite and serpentine had not been obviously reduced in single mineral flotation after the addition of SABMP. The adsorption and ICP results indicated that SABMP could be adsorbed on serpentine surface and simultaneously promote the dissolution of Mg ions on serpentine surface. Further XPS tests demonstrated that SABMP interacted with the Mg species exposed on the surface of serpentine. In addition, it was discovered that the addition of SABMP changed the zeta potential of serpentine from positive to negative at pH 8.5, which eliminated the hetero-coagulation between pyrite and serpentine. The turbidity test further suggested that SABMP could convert the aggregation to the dispersion between pyrite and serpentine. These results demonstrated that SABMP is a potential depressant in the selective flotation separation of pyrite from serpentine.
Sheng-Qiang Guo, Hui-Qing Yang, Yu-Zhen Jiang, Ai-Lian Wang, Guo-Qiang Xu, Yong-Chun Luo, Zhao-Xu Chen, Haixue Zheng and Peng-Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2GC00224H
Multicomponent diastereoselective synthesis is still very difficult to be achieved in photoredox catalysis. Here we report a green and reliable strategy for the diastereoselective synthesis of β-amido sulfones through the organophotoredox catalytic fourcomponent radical-polar crossover cascade reactions. This transformation features excellent atom-, step-, redox economy and diastereoselectivity. Moreover, DFT calculation studies are performed to provide some insights into the orign of diastereoselectivity.

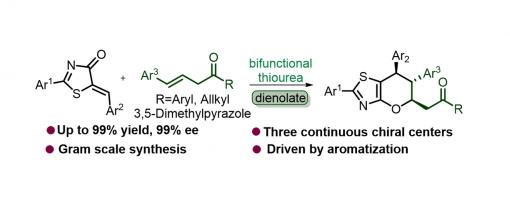
Kai-Xuan Yang, Dong-Sheng Ji, Haixue Zheng, Yucheng Gu* and Peng-Fei Xu *
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CC00457G
An inverse-electron-demand oxa-Diels–Alder reaction of 5-alkenyl thiazolones with β,γ-unsaturated carbonyl compounds enabled by quinine thiourea was studied, which allows the enantioselective synthesis of a broad range of highly functionalized pyranthiazoles bearing three continuous stereocenters. This protocol is adaptable to a wide scope of substrates and has great potential for scale-up synthesis and facile transformation.
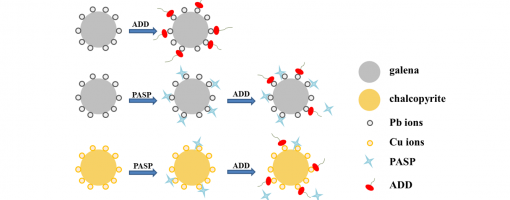
Jie Zhang, Xu-Gang Zhang, Xiang-Xiang Wei, Shao-Yi Cheng, Xiu-Qin Hu, Yong-Chun Luo* Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107464
In the flotation separation of copper-lead–zinc complex polymetallic sulphide ores, the separation of chalcopyrite from galena is difficult because both of them have good floatability. Therefore, the development of a green, eco-friendly and selective galena depressant is highly required. In this work, sodium polyaspartate (PASP) was used as a galena depressant in the separation of chalcopyrite from galena. Single mineral flotation experiments showed that PASP could selectively depress galena. With 10 mg/L PASP addition at pH = 10, the recovery of chalcopyrite remained 91.9%, but the recovery of galena decreased to 1.1%. The selective depression mechanism of PASP was studied by collector adsorption measurements, FT-IR and XPS analysis.
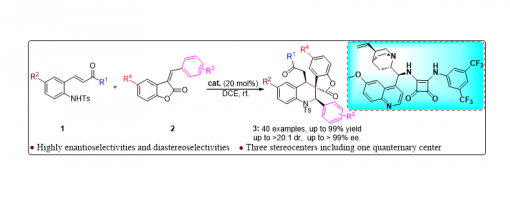
Enantioselective Construction Of Spiro-Tetrahydroquinoline Scaffolds Through Asymmetric Catalytic Cascade Reactions
Jia-Lu Zhang, Rui Ma, Huan-Huan Zhao, Peng-Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CC00502F
Abstract
An efficient and concise strategy has been successfully developed for merging spiro-tetrahydroquinoline with spiro-benzofuranone into a single new skeleton through asymmetric catalytic cascade reactions catalyzed by quinine-derived chiral bifunctional squaramide organocatalysts. In this approach, differently substituted spiro-tetrahydroquinoline derivatives were smoothly obtained with high yields, and excellent diastereoselectivities and enantioselectivities (up to 99% yield, up to >20 : 1 dr, up to >99% ee, 40 examples) under mild reaction conditions.
Organic Photoredox Catalytic Amino-Heteroarylation Of Unactivated Olefins To Access Distal Amino Ketones
Ji-Hua Zhang, Teng-Fei Xiao, Zi-Qin Ji, Han-Nan Chen, Pen-Ji Yan, Yong-Chun Luo, Peng-Fei Xu and Guo-Qiang Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC07189K
Abstract
Here we describe a metal-free amino-heteroarylation of unactivated olefins via organic photoredox catalysis, providing a concise and efficient approach for the rapid synthesis of various δ (β, ε)-amino ketones under mild conditions. This protocol demonstrates that the new photocatalyst Cz-NI developed by our group has an excellent photoredox catalytic performance. Finally, a series of mechanistic experiments and DFT calculations indicate that this transformation undergoes a photoredox catalytic sequential radical addition/functional group migration process.

Solvent Directed Chemically Divergent Synthesis Of β-lactams And α-amino Acid Derivatives With Chiral Isothiourea
Dong-Sheng Ji, Hui Liang, Kai-Xuan Yang, Zhi-Tao Feng, Yong-Chun Luo, Guo-Qiang Xu, Yucheng Gu, Peng-Fei Xu
https://doi.org/10.1039/d1sc06127e
Abstract
A protocol for the chemically divergent synthesis of β-lactams and α-amino acid derivatives with isothiourea (ITU) catalysis by switching solvents was developed. The stereospecific Mannich reaction occurring between imine and C(1)-ammonium enolate generated zwitterionic intermediates, which underwent intramolecular lactamization and afforded β-lactam derivatives when DCM and CH3CN were used as solvents. However, when EtOH was used as the solvent, the intermediates underwent an intermolecular esterification reaction, and α-amino acid derivatives were produced. Detailed mechanistic experiments were conducted to prove that these two kinds of products came from the same intermediates. Furthermore, chemically diversified transformations of β-lactam and α-amino acid derivatives were achieved.

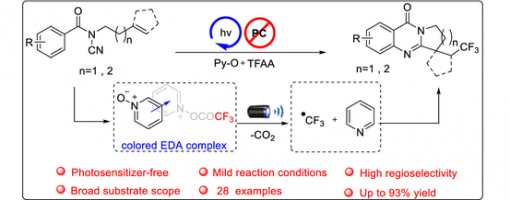
A Photosensitizer–Free Radical Cascade for Synthesizing CF3-Containing Polycyclic Quinazolinones with Visible Light
Qiang Hu, Wan-Lei Yu, Yong-Chun Luo, Xiu-Qin Hu*, and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.1c02889
Abstract
Herein, we report an efficient photoinduced radical tandem trifluoromethylation/cyclization reaction of N-cyanamide alkenes for the synthesis of functionalized quinazolinones. Importantly, the reaction is carried out under mild conditions without any additional photosensitizer, metal, or extra additives. A series of trifluoromethyl quinazolinones were prepared efficiently with good yields and excellent functional group tolerance. Preliminary mechanistic experiments were conducted to indicate that the transformation proceeds via a possible mechanism involving photoexcited EDA complex and chain propagation.
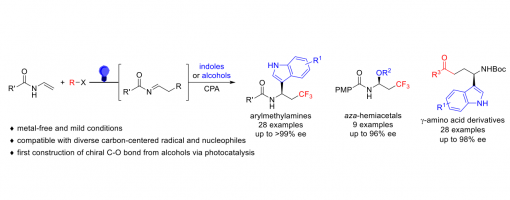
Metal-Free, Visible-Light Induced Enantioselective Three-Component Dicarbofunctionalization And Oxytrifluoromethylation Of Enamines Via Chiral Phosphoric Acid Catalysis
Hui Liang, Dong-Sheng Ji, Guo-Qiang Xu, Yong-Chun Luo, Hai-Xue Zheng* and Peng-Fei Xu *
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1SC06613G
Abstract
Using diverse carbon-centered radical precursors and electron-rich (hetero)aromatics and alcohols as nucleophiles, a visible-light driven chiral phosphoric acid (CPA) catalyzed asymmetric intermolecular, three-component radical-initiated dicarbofunctionalization and oxytrifluoromethylation of enamines was developed, which provides a straightforward access to chiral chiral arylmethylamines aza-hemiacetals and γ-amino acid derivatives with excellent enantioselectivity. As far as we know, this is the first example of constructing a chiral C-O bond using simple alcohols via visible-light photocatalysis. Chiral phosphoric acid played multiple roles in the reaction, including controlling the reaction stereoselectivity and promoting the generation of radical intermediates by activating Togni’s reagent. Mechanistic studies also suggested the importance of the N-H bond of the enamine and indole for the reactions.
Selective Flotation Separation Of Chalcopyrite From Talc By A Novel Depressant: N-methylene Phosphonic Chitosan
Wen-Long Ye, Xu-Gang Zhang, Cheng-Lin Pan, Xiu-Qin Hu*, Yong-Chun Luo*, Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2021.107367
In this work, we investigated the flotation performance and selective adsorption mechanism of a chitosan derivative NMPC (N-methylene phosphonic chitosan) as an novel talc depressant in the flotation separation of chalcopyrite from talc. The single mineral flotation experiments demonstrated that without the talc depressant, both chalcopyrite and talc showed excellent floatability, thus the separation was difficult in the pH range of 3–11. When NMPC was added, the recovery of talc was reduced drastically but the recovery of chalcopyrite decreased slightly in the pH range of 3–9 at a concentration of 10 mg/L in pulp. Artificial mixed mineral flotation experiments also demonstrated that the effective separation of talc and chalcopyrite could be achieved when NMPC was employed as the depressant. The results showed that better grade and recovery were obtained in different proportions of chalcopyrite and talc, which meant the NMPC is better than CMC, Arabic gum in flotation separation of talc and chalcopyrite. Analysis of adsorption tests, FT-IR measurements, and XPS measurements suggested that NMPC was selectively adsorbed on the talc surface by physical adsorption which might result from the hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interaction between NMPC and talc. Moreover, the sedimentation experiments disclosed that NMPC plays an important role in the flocculation and settling of fine talc.
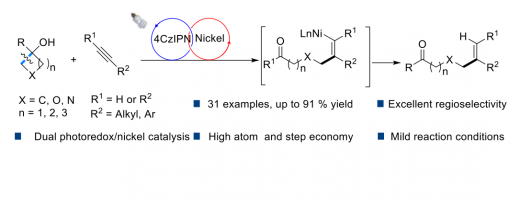
Photoredox/Nickel Dual Catalyzed Stereospecific Synthesis Of Distal Alkenyl Ketones
Tian-Tian Zhao, Wan-Lei Yu, Zhi-Tao Feng, Hao-Ni Qin, Hai-xue Zheng* and Peng-Fei Xu*
https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CC06566A
The selective C–C bond deconstruction/refunctionalization via a photoredox/nickel dual-catalyzed hydroalkylation of alkynes is developed under mild reaction conditions. In this protocol, a broad range of alkyl- and aryl-alkynes could react smoothly with cycloalkanols, affording the corresponding distal and site-specific vinyl-substituted ketones with high yields and excellent regioselectivities. Moreover, DFT calculations verified that the electron-rich behavior of aromatics and weak Brønsted bases have a common effect on the photocatalytic oxidant ring-opening of cyclobutanols.